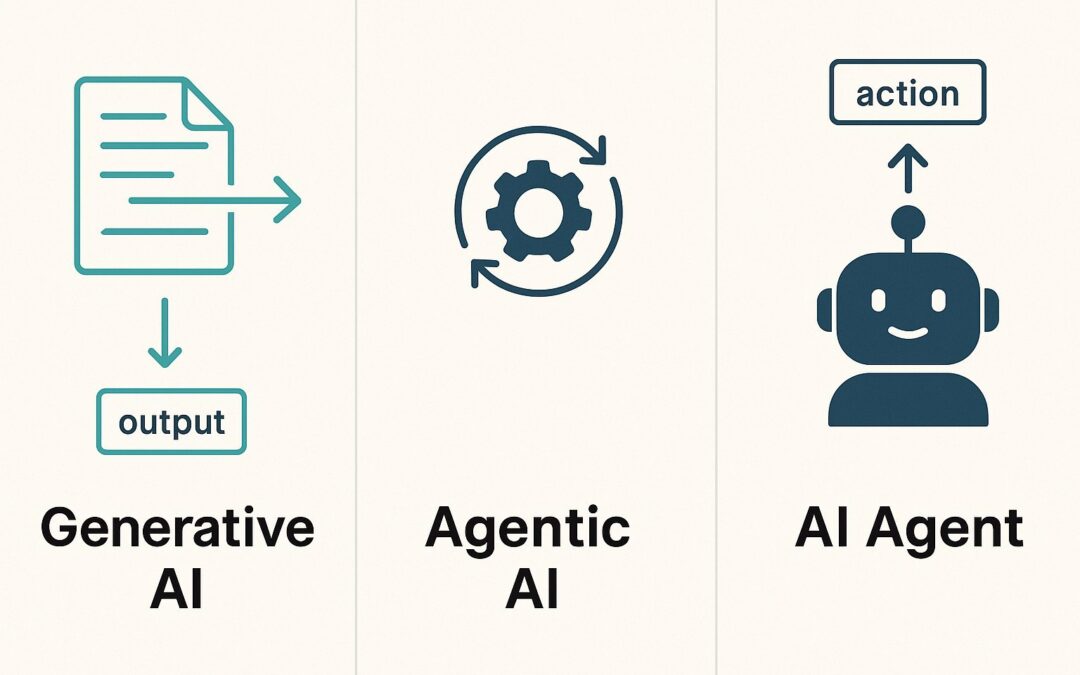
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming how we work and live. As AI becomes more integrated into our daily lives, understanding the nuances between different types of AI is crucial. Two terms that often come up are AI Agents and Agentic AI. While they sound similar, they represent distinct approaches to AI. Adding another layer to the mix is Generative AI, a powerful tool that both AI Agents and Agentic AI can leverage. Let’s break down these concepts in simple terms.
What is an AI Agent ?
Imagine a virtual assistant that follows your commands to send a message or schedule a meeting. That’s an AI Agent. An AI agent is a program designed to perform specific tasks. It operates in a predetermined manner, following instructions to accomplish its objectives. Think of it as a helpful tool that handles simple, repetitive jobs.
Features of AI Agents:
- Limited Freedom: AI agents only execute predefined tasks. They require clear instructions or human input to function
- Focused Tasks: They are designed for specific jobs, such as answering questions or performing small, well-defined actions
- Basic Actions: They react to inputs but lack the ability to think or adapt significantly on their own
Examples:
- Email tools like Gmail’s Smart Reply, which suggests quick responses
- Shopping bots on platforms like Amazon, which recommend products or track orders.
- Characters in video games that follow set patterns
What is Agentic AI ?
Now, think of the same assistant not only sending emails but also planning your day, sending follow-up emails, updating project statuses, writing reports, and even making decisions without requiring constant input. That’s Agentic AI. It’s a more advanced, independent form of AI. It can reason, plan, and make decisions autonomously to tackle larger, more complex problems. Instead of merely executing single tasks, it determines how to achieve a goal by adapting and utilizing various tools.
Features of Agentic AI :
- High Degree of Freedom: It operates without constant human supervision
- Complex Goals: It addresses large tasks by breaking them down into smaller, manageable steps
- Adaptability: It learns and adjusts its plans as it progresses
- Intelligent Reasoning: It synthesizes information, formulates plans, and solves challenging problems
Examples:
- AI that reads patient data, suggests treatments, and organizes hospital schedules
- Systems that execute high-speed stock trades by monitoring market fluctuations
- AI that identifies threats, triggers alerts, and modifies security protocols to maintain safety
How Does Generative AI Fit In ?
Think of Generative AI as the creative engine that powers both AI Agents and Agentic AI. It’s the type of AI that can generate new content – text, images, code, audio, and more.
- AI Agents can use Generative AI: An AI agent tasked with responding to customer inquiries could use a Generative AI model to draft personalized and creative responses.
- Agentic AI can orchestrate Generative AI: An Agentic AI system designed for marketing could use Generative AI to create ad copy, design visuals, and generate social media posts.
| Feature | AI Agents | Agentic AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Executes specific, predefined tasks | Plans, decides, and executes complex goals | Creates new, original content. |
| Autonomy | Low; requires clear instructions | High; can operate independently to achieve goals | N/A (it's a capability that can be used by agents) |
| Scope | Narrow; focused on individual tasks | Broad; tackles complex, multi-step problems | Focused on content creation within specific domains |
| Thinking | Reactive; responds to inputs | Proactive; plans, reasons, and adapts | Generates novel outputs based on learned patterns |
| Examples | Smart Reply, product recommendation bots. | Autonomous vehicles, AI-powered research assistants | ChatGPT (text), DALL-E (images), code generators |
| Relationship | Can use Generative AI for specific tasks | Can orchestrate the use of Generative AI tools | Can be used by both AI Agents and Agentic AI |
Why it matter ?
Understanding the differences between AI Agents, Agentic AI, and Generative AI is crucial for several reasons:
- Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness: AI agents excel at automating routine tasks, freeing up human workers for more strategic roles. Agentic AI can manage entire systems, leading to even greater time and cost savings.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Agentic AI is better suited for complex challenges that require intelligent decision-making, such as in healthcare and finance.
- Safety and Ethical Considerations: The autonomous nature of Agentic AI necessitates careful consideration of safety and ethical implications. Clear guidelines and regulations are essential.
- Future Potential: The combination of Agentic AI’s autonomous decision-making with Generative AI’s creative abilities could lead to incredibly sophisticated and helpful AI systems.
Real-World Applications
- AI Agents in Everyday Life:
- Emails: Tools like Gmail’s Smart Reply suggest quick responses
- Shopping: Bots on Amazon recommend products or track your orders
- Games: Characters in video games that follow set patterns to challenge players
- Agentic AI in Complex Scenarios:
- Healthcare: AI that analyzes patient data, suggests treatments, and organizes hospital schedules
- Finance: Systems that execute high-speed stock trades by monitoring market changes
- Security: AI that identifies threats, triggers alerts, and modifies security protocols to maintain safety
The Power of Collaboration
AI agents can act as building blocks for Agentic AI. For example, in customer service, one AI agent might read a customer’s message, another locate the customer’s order, and a third process a refund – all orchestrated by an Agentic AI system to ensure a seamless experience.
This collaborative approach makes Agentic AI incredibly powerful for handling complex tasks. As AI technology evolves, Agentic AI systems will likely incorporate tools like chat AI, machine learning, and specialized apps to achieve even more.
Looking Ahead
The distinction between AI Agents, Agentic AI, and Generative AI will have a profound impact on the future:
- Job Market Transformation: Agentic AI can automate complex tasks, potentially shifting the focus of human labor towards more creative and strategic endeavors
- Technological Innovation: Agentic AI is driving innovation in various fields, including robotics, medicine, and finance, leading to more efficient and user-friendly solutions
- Ethical Considerations: As Agentic AI becomes more sophisticated, ensuring its responsible and ethical development is paramount
- Widespread Adoption: Agentic AI has the potential to be integrated into numerous industries and even our homes, while AI agents will continue to excel in more focused, task-oriented applications
Conclusion
AI Agents and Agentic AI represent distinct approaches to AI, each with its strengths. AI agents are ideal for automating simple, repetitive tasks, while Agentic AI is designed for complex, multifaceted challenges. Generative AI is a powerful tool that both can leverage to enhance their capabilities. Understanding these differences is key to harnessing the power of AI effectively and preparing for the future. As AI continues to evolve, particularly with the integration of Generative AI, it has the potential to reshape our lives and work in profound ways.